Chris Richardson 的微服务架构网站
本站由 Kong 提供支持微服务架构咨询和培训服务
本站点由 Chris Richardson 编写和维护,他是经典技术著作《POJOS IN ACTION》一书的作者,也是 cloudfoundry.com 最初的创始人。Chris 的研究领域包括 Spring、Scala、微服务架构设计、领域驱动设计、NoSQL 数据库、分布式数据管理、事件驱动的应用编程等。Chris 是一位连续创业者,eventuate.io 是他的最新创业项目,一个微服务应用和数据服务平台。
Chris 定期为企业提供微服务设计培训和实战项目的架构咨询服务。近年来 Chris 多次访问中国,为包括华为、SAP、惠普、东风汽车等大型企业提供微服务架构相关的技术咨询服务。如您希望与 Chris 深入交流,建立合作,请点击下方按钮跟他取得联系。
模式库
核心模式
服务拆分
部署模式
需要关注的边界问题
通讯模式
数据管理
安全模式
- 访问令牌new
可测试性
可观测性
UI 模式
- 服务器端页面碎片化元素构建new
- 客户端 UI 构建new

全新的微服务应用支撑平台,成功解决微服务架构下分布式数据管理的难题。
加入 微服务架构的 Google 讨论组(需要翻墙)
Pattern: Decompose by subdomain
Context
You are developing a large, complex application and want to use the microservice architecture. The microservice architecture structures an application as a set of loosely coupled services. The goal of the microservice architecture is to accelerate software development by enabling continuous delivery/deployment.
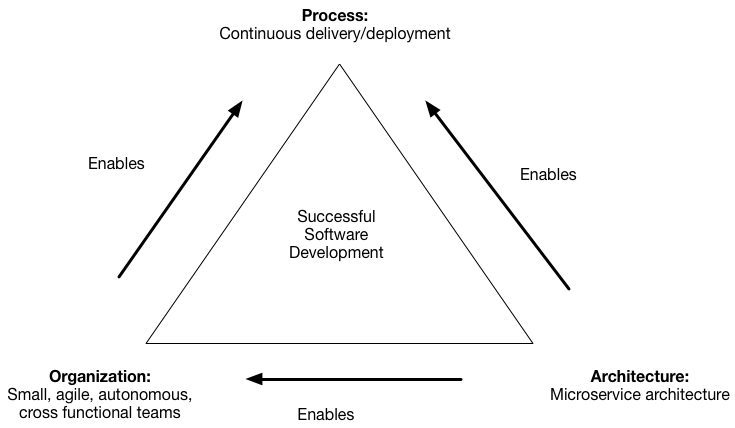
The microservice architecture does this in two ways:
- Simplifies testing and enables components to deployed independently
- Structures the engineering organization as a collection of small (6-10 members), autonomous teams, each of which is responsible for one or more services
These benefits are not automatically guaranteed. Instead, they can only be achieved by the careful functional decomposition of the application into services.
A service must be small enough to be developed by a small team and to be easily tested. A useful guideline from object-oriented design (OOD) is the Single Responsibility Principle (SRP). The SRP defines a responsibility of a class as a reason to change, and states that a class should only have one reason to change. It make sense to apply the SRP to service design as well and design services that are cohesive and implement a small set of strongly related functions.
The application also be decomposed in a way so that most new and changed requirements only affect a single service. That is because changes that affect multiple services requires coordination across multiple teams, which slows down development. Another useful principle from OOD is the Common Closure Principle (CCP), which states that classes that change for the same reason should be in the same package. Perhaps, for instance, two classes implement different aspects of the same business rule. The goal is that when that business rule changes developers, only need to change code in a small number - ideally only one - of packages. This kind of thinking makes sense when designing services since it will help ensure that each change should impact only one service.
Problem
How to decompose an application into services?
Forces
- The architecture must be stable
- Services must be cohesive. A service should implement a small set of strongly related functions.
- Services must conform to the Common Closure Principle - things that change together should be packaged together - to ensure that each change affect only one service
- Services must be loosely coupled - each service as an API that encapsulates its implementation. The implementation can be changed without affecting clients
- A service should be testable
- Each service be small enough to be developed by a “two pizza” team, i.e. a team of 6-10 people
- Each team that owns one or more services must be autonomous. A team must be able to develop and deploy their services with minimal collaboration with other teams.
Solution
Define services corresponding to domain-driven design subdomains
Related patterns
- The Decompose by business capability pattern is an alternative pattern