Pattern: Decompose by subdomain
patternContext
You are developing a large, complex application and want to use the microservice architecture. The microservice architecture structures an application as a set of loosely coupled services. The goal of the microservice architecture is to accelerate software development by enabling continuous delivery/deployment.
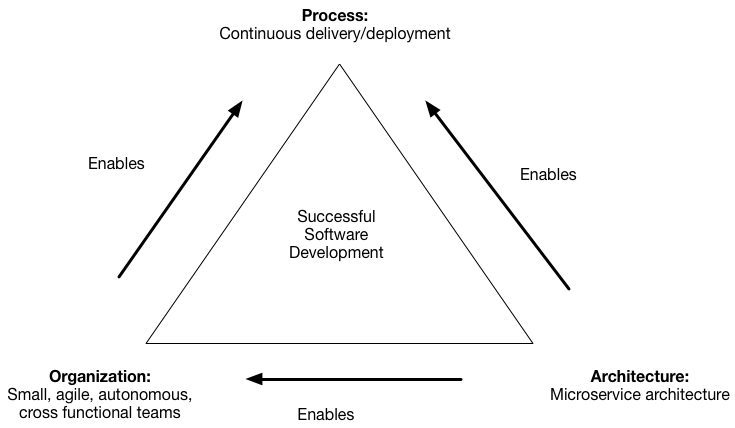
The microservice architecture does this in two ways:
- Simplifies testing and enables components to deployed independently
- Structures the engineering organization as a collection of small (6-10 members), autonomous teams, each of which is responsible for one or more services
These benefits are not automatically guaranteed. Instead, they can only be achieved by the careful functional decomposition of the application into services.
A service must be small enough to be developed by a small team and to be easily tested. A useful guideline from object-oriented design (OOD) is the Single Responsibility Principle (SRP). The SRP defines a responsibility of a class as a reason to change, and states that a class should only have one reason to change. It make sense to apply the SRP to service design as well and design services that are cohesive and implement a small set of strongly related functions.
The application also be decomposed in a way so that most new and changed requirements only affect a single service. That is because changes that affect multiple services requires coordination across multiple teams, which slows down development. Another useful principle from OOD is the Common Closure Principle (CCP), which states that classes that change for the same reason should be in the same package. Perhaps, for instance, two classes implement different aspects of the same business rule. The goal is that when that business rule changes developers, only need to change code in a small number - ideally only one - of packages. This kind of thinking makes sense when designing services since it will help ensure that each change should impact only one service.
Problem
How to decompose an application into services?
Forces
- The architecture must be stable
- Services must be cohesive. A service should implement a small set of strongly related functions.
- Services must conform to the Common Closure Principle - things that change together should be packaged together - to ensure that each change affect only one service
- Services must be loosely coupled - each service as an API that encapsulates its implementation. The implementation can be changed without affecting clients
- A service should be testable
- Each service be small enough to be developed by a “two pizza” team, i.e. a team of 6-10 people
- Each team that owns one or more services must be autonomous. A team must be able to develop and deploy their services with minimal collaboration with other teams.
Solution
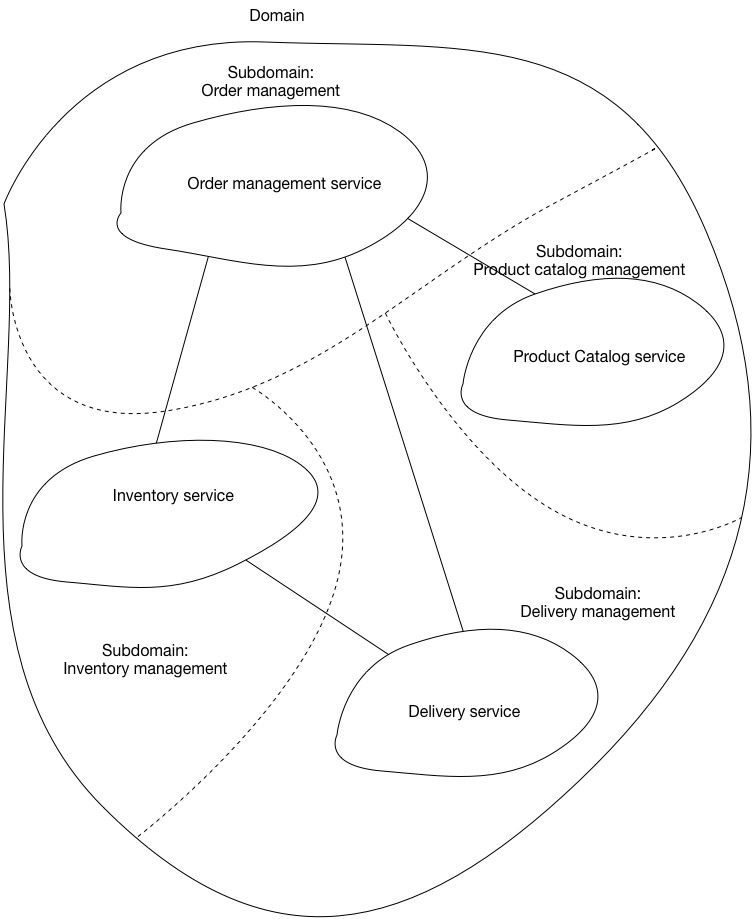
Define services corresponding to Domain-Driven Design (DDD) subdomains. DDD refers to the application’s problem space - the business - as the domain. A domain is consists of multiple subdomains. Each subdomain corresponds to a different part of the business.
Subdomains can be classified as follows:
- Core - key differentiator for the business and the most valuable part of the application
- Supporting - related to what the business does but not a differentiator. These can be implemented in-house or outsourced.
- Generic - not specific to the business and are ideally implemented using off the shelf software
Examples
The subdomains of an online store include:
- Product catalog
- Inventory management
- Order management
- Delivery management
- …
The corresponding microservice architecture would have services corresponding to each of these subdomains.
Resulting Context
This pattern has the following benefits:
- Stable architecture since the subdomains are relatively stable
- Development teams are cross-functional, autonomous, and organized around delivering business value rather than technical features
- Services are cohesive and loosely coupled
Issues
There are the following issues to address:
-
How to identify the subdomains? Identifying subdomains and hence services requires an understanding of the business. Like business capabilities, subdomains are identified by analyzing the business and its organizational structure and identifying the different areas of expertise. Subdomains are best identified using an iterative process. Good starting points for identifying subdomains are:
- organization structure - different groups within an organization might correspond to subdomains
- high-level domain model - subdomains often have a key domain object
Related patterns
- The Decompose by business capability pattern is an alternative pattern


 Premium content now available for paid subscribers at
Premium content now available for paid subscribers at